Equity vs. Options: Which One Should You Choose?
- Pankaj Singh
- Sep 6, 2024
- 4 min read
When deciding to invest in the stock market, you may come across two popular types of investment instruments: equities (or stocks) and options. Both can offer opportunities for profit, but they come with different risks, rewards, and strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial to making the right choice for your financial goals. In this article, we will explore what equities and options are, how they work, and which might be the better choice for you.
What Are Equities?
Equities, also known as stocks, represent ownership in a company. When you buy a share of a company, you essentially own a small piece of that business. As a shareholder, you have the potential to earn money in two primary ways:
Capital Appreciation: If the company performs well, the value of its stock may increase over time, allowing you to sell your shares for a profit.
Dividends: Some companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends, providing a steady stream of income.
Pros of Investing in Equities:
Ownership: You own a part of the company and can benefit from its growth.
Long-Term Growth: Historically, equities have provided significant long-term returns compared to other asset classes.
Dividends: Potential to earn regular income through dividends, depending on the company's policy.
Liquidity: Equities are generally easy to buy and sell on the stock market.
Cons of Investing in Equities:
Market Volatility: Stock prices can be highly volatile and are influenced by various factors such as economic conditions, company performance, and market sentiment.
No Guaranteed Returns: There is no guarantee of returns, and investors may lose their initial investment if the company performs poorly.
Risk of Loss: Stocks can decline in value, leading to potential financial losses.
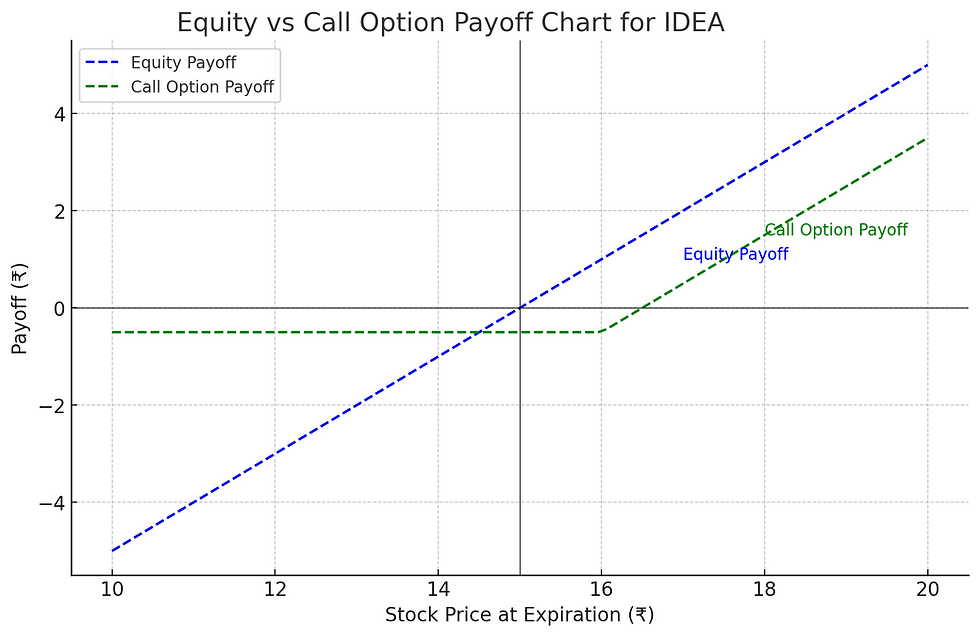
What Are Options?
Options are financial derivatives that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. There are two main types of options:
Call Options: Gives the holder the right to buy a stock at a certain price (known as the strike price) before a specific date.
Put Options: Gives the holder the right to sell a stock at a certain price before a specific date.
Pros of Investing in Options:
Leverage: Options allow you to control a large number of shares with a relatively small investment, amplifying potential returns.
Flexibility: Options can be used to speculate on price movements, hedge against potential losses, or generate income through various strategies.
Limited Risk for Buyers: The maximum loss for an options buyer is limited to the premium paid for the option.
Cons of Investing in Options:
Complexity: Options require a deep understanding of financial markets and the various strategies involved. They are not as straightforward as equities.
High Risk for Sellers: While buyers have limited risk, sellers (or writers) of options can face substantial losses if the market moves against them.
Expiration: Options have an expiration date, after which they become worthless. Timing is crucial in options trading.
Potential for Significant Losses: Due to leverage, losses can be magnified, especially if the market moves in an unfavorable direction.
Equity vs. Options: Key Differences
Feature | Equities | Options |
|---|---|---|
Ownership | Provides ownership in a company | No ownership; only the right to buy/sell |
Risk Level | Moderate to high (depends on the stock) | High, especially if strategies are misunderstood |
Potential Returns | Potential for long-term gains | Potential for high returns but also high risk |
Complexity | Relatively simple | Requires deeper market knowledge |
Investment Horizon | Suitable for long-term investments | Can be used for short-term strategies |
Liquidity | Highly liquid; easy to buy and sell | Varies; some options can be less liquid |
Time Sensitivity | Not time-sensitive; can hold indefinitely | Highly time-sensitive due to expiration |
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between equities and options depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and knowledge level.
Choose Equities If:
You are a beginner investor looking for a straightforward and relatively stable investment.
You are interested in long-term growth and are willing to hold investments for several years.
You prefer a lower-risk approach with the potential for steady returns through capital appreciation and dividends.
You want to invest in specific companies that you believe have strong future potential.
Choose Options If:
You are an experienced investor with a solid understanding of the stock market and options strategies.
You are looking for short-term opportunities to profit from market volatility.
You have a high-risk tolerance and are comfortable with the potential for significant gains or losses.
You want to hedge your existing investments or speculate on future price movements without committing a large amount of capital.
Conclusion
Both equities and options offer unique opportunities and risks. If you are new to investing or prefer a more straightforward approach with potentially lower risk, equities may be the better choice. However, if you have the experience, knowledge, and risk tolerance to handle more complex investments, options can provide greater flexibility and the potential for higher returns. Always consider your financial goals and consult with a financial advisor if you are unsure which investment is right for you.

Comments